PREVENTION PROGRAM
Improving collective well-being
Reduce your workers' noise exposure!

By Hany Ghonaim | Founder at ODYO
Early detection of excessive noise within a company is an important step in limiting the risk of hearing loss among workers. When noise levels exceed thresholds deemed safe, prompt action can prevent irreversible damage to the inner ear. In fact, the earlier the intervention, for example, by implementing protective measures or noise reduction, the more the health consequences will be limited.
This article highlights the risks and consequences of delaying action, while explaining the lasting benefits of a hearing prevention policy. It concludes with a presentation of concrete ways to take action and effectively reduce noise exposure.
Consequences of noise
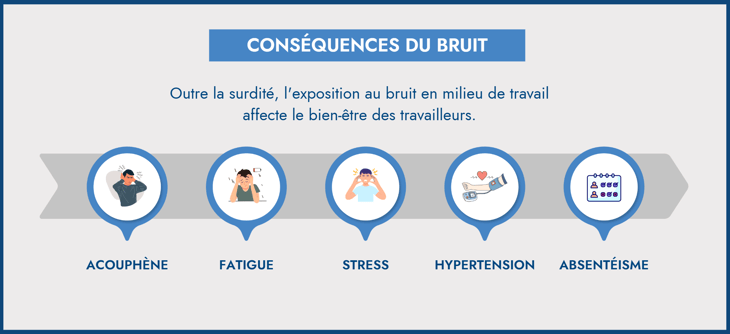
Exposure to noise in the workplace affects workers' well-being. Here are the various consequences of noise in the workplace:
-
Occupational deafness: This is a disease that generally develops during the first ten to fifteen years of exposure to noise. It occurs when the inner ear, and in particular the hair cells, are damaged by prolonged or repetitive exposure to loud sounds. Hearing fatigue may initially be temporary, but may become permanent if exposure continues. Over time, hearing loss gradually sets in, and may be accompanied by tinnitus.
-
Tinnitus : Tinnitus is a symptom that often manifests itself after prolonged exposure to loud noises. It is characterized by whistling or buzzing noises that can intensify after continuous exposure to noise.
-
Fatigue : Fatigue caused by exposure to noise in the workplace can result in increased irritability, reduced concentration and a general feeling of exhaustion.
-
Stress : Continuous exposure to noise in the workplace can generate chronic stress, leading to headaches and sleep disturbances, which in turn aggravate feelings of fatigue.
-
Hypertension : Prolonged exposure to noise in the workplace can increase blood pressure, leading to hypertension. Constant noise keeps the body in a state of heightened alertness, stimulating the release of stress hormones. Over time, this constant state of stress can impair the cardiovascular system and increase the risk of heart disease.
-
Absenteeism : Excessive exposure to noise in the workplace can lead to chronic fatigue and increased stress, with a direct impact on employee health and morale. This can translate into headaches, irritability and an overall sense of weariness, leading some workers to miss work more frequently. In the long term, noise-related absenteeism disrupts team functioning and has repercussions on company productivity.
Professional deafness
The more frequent and sustained the exposure to noise, the greater the risk of hearing loss deterioration. Regulations and experts in the field consider that continuous exposure to 85 dB or more, over an eight-hour period, can trigger a degradation process in the fragile hair cells of the inner ear. Reverberation of sound in enclosed spaces, exposure to toxic substances, vibration and lack of hearing protection all increase the risk of hearing loss.
OVERVIEW OF HEARING LOSS IN THE WORKPLACE

In Quebec, occupational deafness is one of the most common workplace injuries. The number of cases accepted by the Commission des Normes, de l'Équité, de la Santé et de la Sécurité au Travail (CNESST) is increasing exponentially every year, reaching an annual average of over 10,000 cases since 2013.


The consequences of occupational deafness manifest themselves in different ways. Physiologically, it results in impaired hearing of high-pitched sounds, with the risk of tinnitus. Psychologically, it can cause chronic stress, isolation and communication difficulties, leading to feelings of helplessness and potentially depression. Socio-economically, it translates into lower productivity, an increased risk of accidents due to reduced perception of warning signals, and financial costs linked to compensation, hearing aids, rehabilitation and time off work.
And yet, what are we doing as a society to reduce the incidence of this irreversible but equally preventable disease? Perhaps the hole in society's wallet will finally prompt us to plug the one in our ears?
The cost to society of professional deafness
In addition to its individual consequences, occupational deafness has major economic and social repercussions that extend far beyond the company where the injured individual is employed.
Here are some alarming conclusions from a study conducted by theInstitut de recherche Robert-Sauvé en santé et en sécurité du travail (IRSST) on the costs of occupational injuries in Quebec:
- The ear is the4th most costly injury site per year.
- The ear generates the highest average cost per injury.
- Noise exposure is the3rd most costly causalagent per year.
The main costs associated with occupational injuries include medical expenses, lost productivity and human costs. Here's an overview of the costs caused by occupational deafness:

-
Medical costs
-
The cost of purchasing and maintaining hearing aids can be very high.
-
Auditory re-education sessions, sometimes necessary to improve sound perception and comprehension, represent a significant investment for the healthcare system.
-
The treatment of associated disorders, such as anxiety or depression, also adds to the overall cost to society.
-
-
Loss of productivity
-
Workers suffering from occupational deafness often experience a drop in performance, or are forced to switch to less exposed positions, or even take sick leave.
-
-
-
On a provincial or national scale, occupational deafness can have a significant impact on the competitiveness of certain sectors.
-
-
Human costs
-
A hearing-impaired person who is not fitted with a hearing aid can become isolated from community life, which can increase the risk of loneliness, depression and other mental health problems.
- This isolation has an impact on the social fabric, and may require the implementation of support structures to facilitate communication and maintain life in society.
-
In short, occupational deafness has costly consequences for society, in both economic and human terms. Effective preventive measures are therefore urgently needed in noisy working environments.
Benefits of noise prevention measures
Improved collective well-being
A noise-controlled working environment promotes serenity and team motivation. Employees exchange ideas more easily and develop a strong sense of belonging. What's more, by reducing exposure to noise pollution, we limit the onset of related disorders (headaches, anxiety, sleep problems).
Enhanced performance
- Reduced accidents: an employee whose hearing is preserved detects warning signals more easily.
- Improved concentration: less distracted by noise, workers are more focused on their tasks.
- Increased productivity: hearing-healthy teams are often more dynamic and efficient.
Employee loyalty
- Reduced absenteeism: preventing occupational deafness reduces sick leave due to hearing problems.
- Company attractiveness: in a competitive job market, quality working conditions (including good noise control) enhance an employer's reputation.
- Long-term cost containment: by investing early in prevention (protection, adaptation), the company saves on health and compensation costs.
Hearing loss prevention program

Preventing hearing loss in noisy workplaces is an essential lever for public health and collective well-being. The sooner we act, the more we can preserve workers' hearing capital and avoid the harmful consequences of noise on society's physical, mental and economic health.
To ensure optimum protection of workers' hearing, the implementation of a hearing loss prevention program becomes an indispensable ally. Here are the main components to consider:
Assessing noise risk
Measure noise levels using specialized equipment to quickly identify critical areas, while mapping the site and prioritizing interventions as soon as a suspicious or unusual noise is detected.
Reducing noise exposure
To limit noise propagation, we recommend the installation of soundproof partitions or panels, regular maintenance of machinery and equipment to reduce stray noise, reorganization of workspaces to keep quiet areas as far away from noise sources as possible, and the provision of earplugs and earmuffs adapted to the noise intensity of the working environment.
Audiometric tests
To detect hearing problems early, we recommend regular audiometric tests. This enables proactive monitoring of hearing, rapid intervention if necessary, and helps prevent further deterioration, ensuring a better quality of life.
Training and awareness-raising
Plan training sessions to make staff aware of the dangers of noise both on and off the job, and stress the importance of wearing and properly maintaining their personal protective equipment to protect against noise.
Controlling results
Plan training sessions to make staff aware of the dangers of noise both on and off the job, and stress the importance of wearing and properly maintaining their personal protective equipment to protect against noise.
Continuous improvement
Plan training sessions to make staff aware of the dangers of noise both on and off the job, and stress the importance of wearing and properly maintaining their personal protective equipment to protect against noise.
Implementing a hearing loss prevention program contributes to a more peaceful, safer and productive work environment. Savings on health and compensation costs, combined with an improved corporate image, create a virtuous circle from which all stakeholders benefit, including employers, employees and society. At the end of the day, protecting your teams' hearing means investing in their quality of life, their safety and the sustainability of your business.
Down with professional deafness!
Rely on our expertise to set up your hearing loss prevention program.


-1.png?width=144&height=72&name=BJA%20_%20Logo%20Color%20%20(1)-1.png)
